Conditions
Getting the Right Treatment
It is important to be diagnosed and treated promptly for any ocular disease, this will also ensure a better response to any treatment. If you have any questions please feel free to contact me.
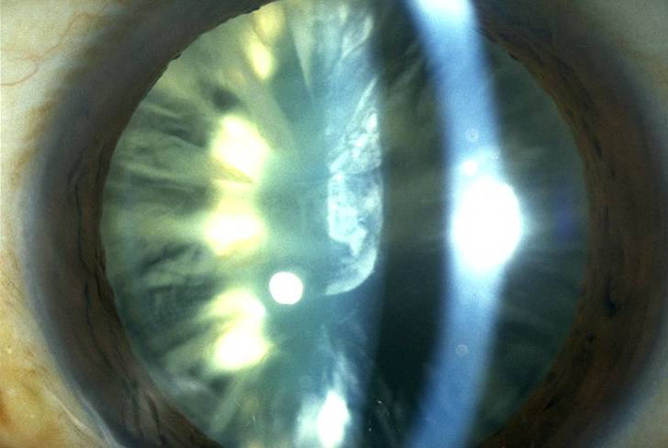
Cataract
This condition occurs when the lens in the eye becomes cloudy, most commonly due to age, inflammation or steroid use. Some cataracts progress rapidly while others develop gradually over time.
Main symptoms of cataracts are blurred vision, glare, reduced colour vision, seeing haloes around lights, and frequently requiring a new pair of glasses or contact lenses.
Cataract Surgery
The only treatment for cataracts is surgery to improve vision. The surgery involves removal of the lens which has now become cloudy due to a cataract.
Your natural lens will be replaced by an artificial lens implant that will remain permanently in your eye. You may still require reading and/or distance glasses post-operatively and this would be dependent on the lens that is implanted in your eye.
A local anaesthetic is administered immediately prior to the surgery. The incision required to perform the cataract operation is usually self-sealing but it may occasionally require suturing. These sutures are normally removed once the eye has healed.
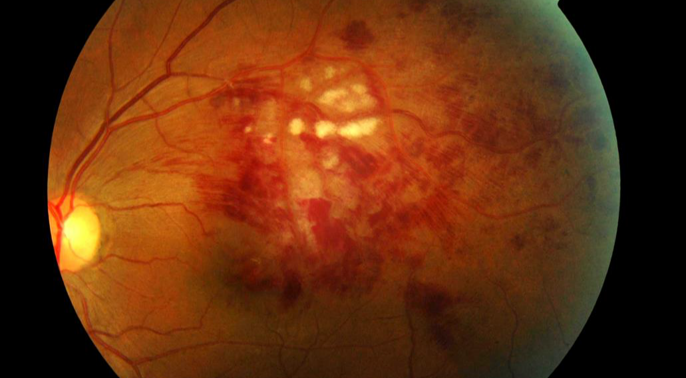
Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
This is an eye disease that affects the macula which is a light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye which is very important for our central vision, colour vision and the fine details that we see.
AMD does not usually cause complete loss of vision, but it can cause a severe reduction in your central vision.
This would make it harder to read, drive, do close work and see faces clearly.
There are two types of AMD; Dry and Wet. Dry AMD is the most common type of AMD. It develops slowly and causes a gradual change in your vision.
Wet AMD is a less common form of AMD, however it can develop more quickly and cause severe sight loss.
Wet AMD is treated with a course of intravitreal anti -VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) injections.

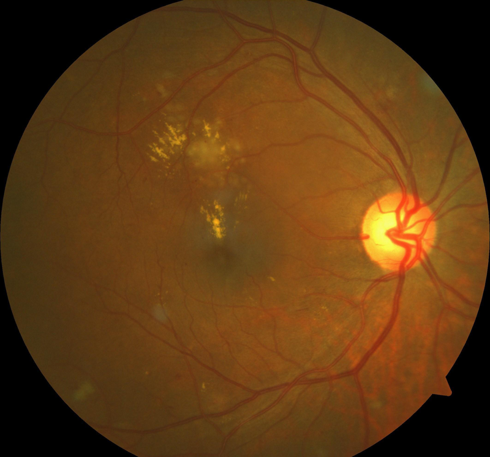
Retinal Vein Oclusion
A retinal vein occlusion is a sudden painless partial or complete blockage in a vein that drains blood from the retina.
The retina is a thin membrane that lines the inner surface of the back of the eye, and it plays an important role in capturing light and translating it into images that you can see.
This condition may require treatment with Intravitreal injections or Laser.
If left untreated there is a high risk of a recurrent vein occlusion as well as a risk to the contralateral eye.
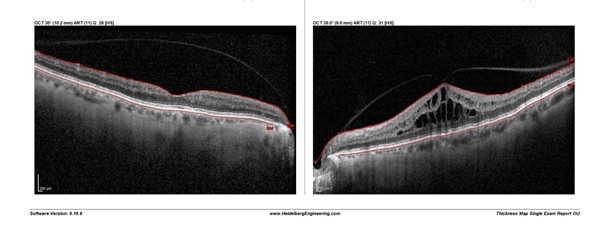
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the blood vessels in the retina.
It is important to have your eyes monitored at regular intervals if you are diabetic as well as maintaining optimum blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
I monitor Diabetic Retinopathy patients and am able to provide treatment for proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Maculopathy.
Disorders of the Retina
This includes any macular conditions, inherited eye disease or degenerative retinal disorders including:
- Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
-
Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy screening
I will assess your eye condition and recommend treatment.
Uveitis (Ocular Inflammation)
Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation which affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea).
Symptoms include pain, blurred vision and redness.
Uveitis can be classified into anterior, intermediate and posterior dependent on which part of the eye is inflamed. Panuveitis occurs when all the layers of the uvea are inflamed.
It can affect children as well as adults and can be associated with autoimmune, infective, or inflammatory conditions of the body. Often no underlying cause is found, although smokers are at a higher risk of uveitis.
The characteristic signs and symptoms of uveitis include a red, painful eye, photosensitivity, blurred vision and floaters in your field of vision. These symptoms can occur suddenly affecting one or both eyes.
If left untreated, Uveitis can cause Glaucoma, Cataracts and Retinal Swelling (Macular Oedema). Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications and preserve your vision.
I can diagnose and manage new and recurrent uveitis.
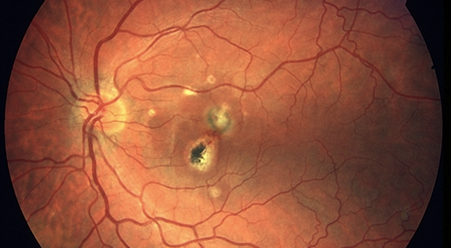
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a condition which damages the optic nerve which is responsible for sending visual information from your eye to the brain. It is often related to high pressure in your eye; however, glaucoma can also occur with normal intraocular pressure. This condition can occur at any age but is more common in adults.
In open angle glaucoma there are usually no visual symptoms, and it is only when the disease is advanced that you perceive an issue with your vision. For example, patchy or blurred vision or reduced peripheral field of vision.
This is why it is very important to have regular Ophthalmic reviews to ensure any glaucoma is diagnosed and treated early.
In acute angle closure glaucoma patients present with a sudden onset of symptoms of headache, eye pain, blurred vision, halos around lights and eye redness. These patients need immediate treatment to prevent loss of vision. A peripheral iridotomy procedure is usually performed to help open the drainage angle and treat or prevent angle-closure glaucoma.
I manage patients who require medical treatment for their glaucoma.
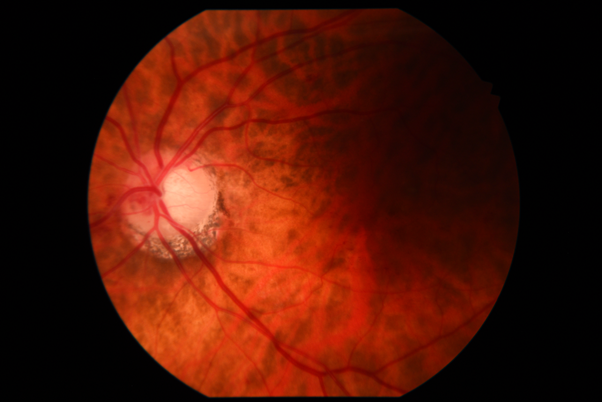
General Ophthalmology
This includes conditions such as:
- Dry eyes
- Cysts of the eyelids
- Blepharitis
- Floaters
- Chalazion removal
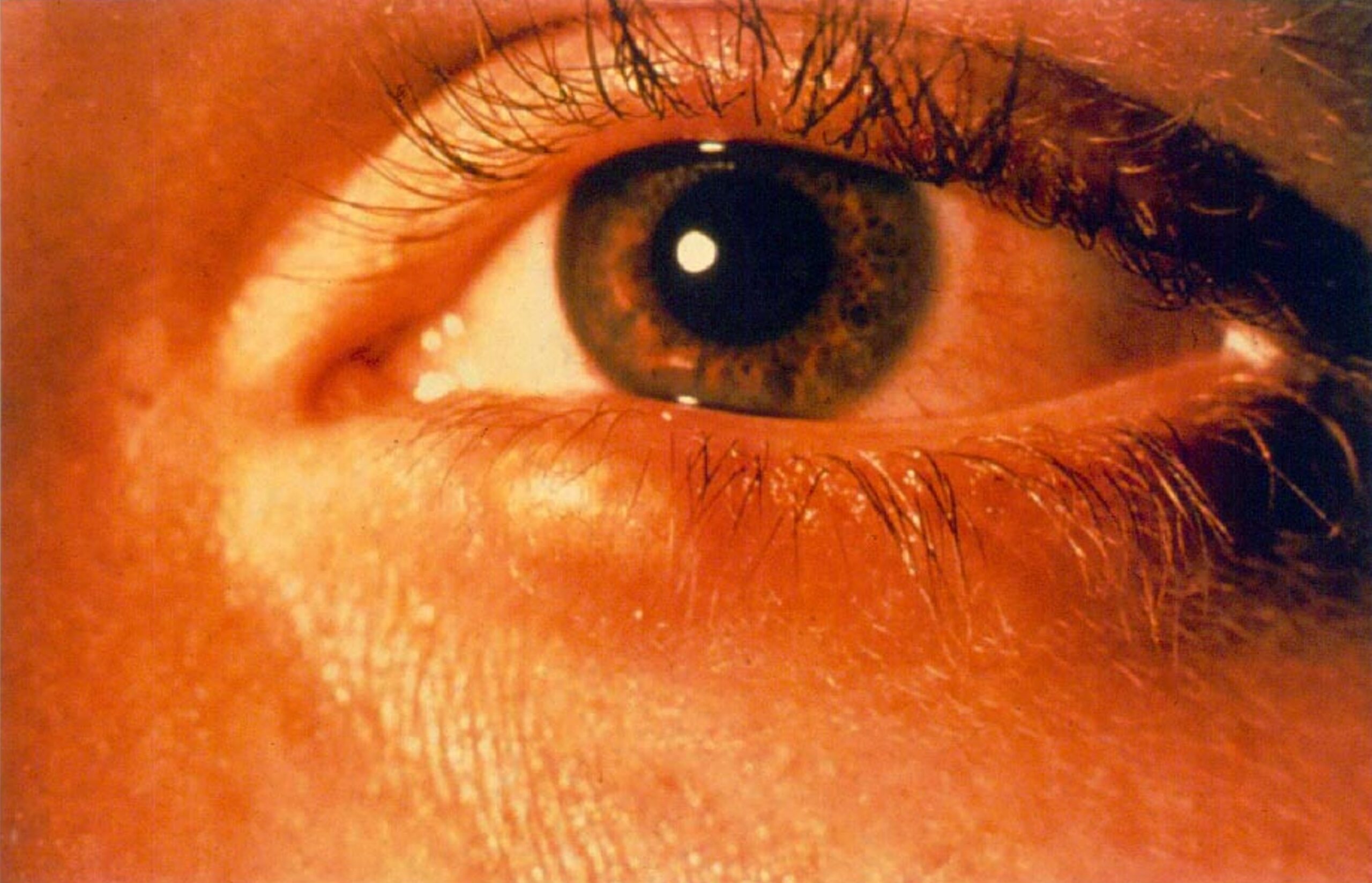
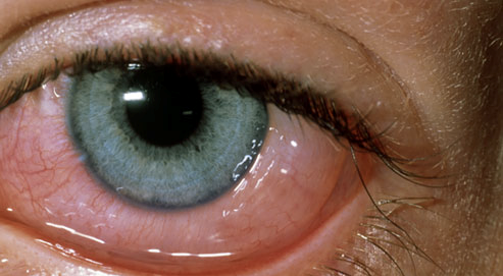
Ocular Emergencies
I am happy to see patients who have developed a red eye or noticed a change in their vision and require immediate Ophthalmic treatment.
The following list is by no means exhaustive but gives an indication of the more common conditions I manage in the acute setting.
- Acute Red Eye
- Conjunctivitis
- Iritis
- Corneal Foreign Body
- Episcleritis/Scleritis
- Corneal Ulceration
- Posterior Vitreous Detachment
- Raised Intraocular Pressure
Professional Affiliations





